Trammel Nets
DescriptionTrammel nets are like gill nets, but they are made of three parallel vertical mesh panels instead of just one. The two outer panels are larger mesh, and the inner panel is composed of smaller-sized mesh. The inner panel has greater depth than the outer panels. Meshes can be made of either monofilament or multifilament or the inner composed of monofilament and the outer multifilament. All panels are sewn to a top and bottom framing line (optimally) or float line on top and a lead line on the bottom. Fishes are captured by entanglement, that is, fish become wrapped in the mesh or caught by a body part (dorsal spine, opercular spine, mouth, etc.). This module emphasizes drifting, benthic trammel nets. | ||||||
| ||||||
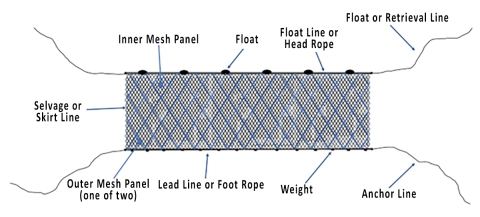
Trammel Net Anatomy | ||||||
Standard Trammel Net (weights may be added for benthic sets or higher current situations when drifting, floats may be added for drift sampling) Trammel net and gill net designs have similarities. Refer to the “Gill Net module” for additional design and anatomy specifics shared between the two types of nets. | ||||||
Common sizes, Materials, Mesh size of drifting benthic trammel nets | ||||||
| ||||||
How trammel nets catch fish | ||||||
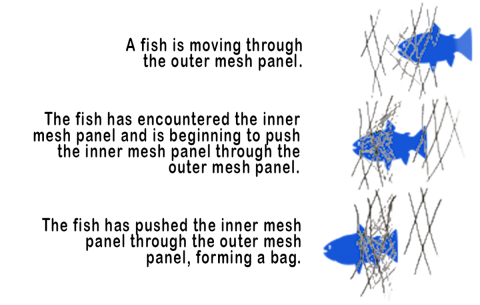
Trammel nets are classified an entanglement gear, so fish capture is accomplished by some form of entanglement. Trammel nets have two primary modes of capture, “bagged” and “gilled”. Fish encountering the net can swim through one of the outer panels, run into the small-mesh middle panel, propel forward, and push the small-mesh inner panel through the other large-mesh outer panel. When this occurs, a bag of small mesh containing the fish is protruded through the large mesh, and the fish is “bagged.” Otherwise, like gill nets, individuals may be entangled by spines or hard structures in the smaller mesh panel (“gilled”). | ||||||
This series of three stages illustrate the process of capturing a fish by “bagging” in a trammel net. | ||||||
Trammel vs. Gill Net FunctionalityRelationship to another entanglement gear, the Gill Net VIDEO: https://youtu.be/OJnXUgg-NEM | ||||||
Gill Net and Trammel Net Storage TipsVIDEO LINK: https://youtu.be/npbLN47XMb0 | ||||||
The referenced media source is missing and needs to be re-embedded. Quick Repairs- Tools, Twines, and Repair Methods: See Repairing Nets Module Replacement rules Fisheries offices may and should have guidelines on when to replace a Trammel net.One example specifies that if a gillnet has a minimum of 25% of the netting area torn, then replace the net. | ||||||
Field Methods | ||||||
Drift length: How deployed: Definitions: See Gill Net module | ||||||
Anatomy, materials, how Trammel nets operate | ||||||
Trammel Net IntroductionIntroduction to Trammel Nets VIDEO LINK: https://youtu.be/EmzPaVtYRps | ||||||
Trammel Net Sizing and ImplicationsDifferent sizes and advantages, advice VIDEO LINK:https://youtu.be/sPg16K8zDiI | ||||||
Dyeing Entanglement NetsDyeing nets VIDEO LINK:https://youtu.be/DM_0Xw6iolA | ||||||
Hobbling Techniques for Drifting Trammel NetsHow a drifting trammel net operates on ridged, uneven sandy bottoms, including modifications to increase catch as by adding weights and hobbling. Also, net drifting directions relative to bottom sandy ridges VIDEO LINK:https://youtu.be/2KhQMAFCwk0 | ||||||
Field Methods, Deployment and Retrieval | ||||||
Preparing to Deploy a Trammel NetTrammel Net (drifting) preparation for deployment VIDEO LINK:https://youtu.be/WKJTXtNi4MY | ||||||
Trammel Net (drifting) deployment and retrieval 1Trammel Net (drifting) deployment and retrieval with snag removals VIDEO LINK: https://youtu.be/jKdAGaBrMfA | ||||||
Trammel Net (drifting) deployment and retrieval 2Trammel Net (drifting) deployment and retrieval VIDEO LINK: https://youtu.be/EkrHtO-Lh9Y | ||||||