|
|
Using Map Coordinates |
It is often useful to know the coordinates of a particular location. Typically, you'll likely be interested in determining the latitude and longitude of a spot on the map. You can do this by looking at the live coordinate display in the bottom-left corner of the Mapper window.
The Coordinates tool has several features that make it easy to work with map coordinates. You can click the map to get the coordinates of the clicked location, display coordinates as you move the mouse on the map, copy coordinates to the Windows clipboard, and convert latitude and longitude to a projected coordinate system.
Be sure to read the Helpful Tip at the bottom of this topic for important information concerning coordinate values and notation.
Getting Started
The Coordinates tool is always displayed in the lower-left corner of the Mapper window, just to the right of the scale bar.

TheCoordinates Tool is to the right of the scale bar
Modes of Operation
The Coordinates tool has two modes of operation:
⚫ Continuous
⚫ Point
The default continuous mode displays a continuous readout of coordinates as you move the mouse cursor around the map. The point mode displays the coordinates of a location in the map that you click on.
To switch between the two modes, click on the Coordinates icon that is shown to the left of the coordinate readout, as illustrated below.
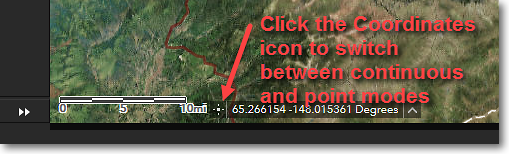
Switching between coordinate readout modes
To See a Continuous Readout of Coordinates
By default, the Coordinates tool displays a continuous readout of coordinates as you move the mouse cursor around the map. This is the default mode; you don't have to do enable the continuous mode.
If you need to make a note of the coordinates at a particular spot on the map, leave the mouse cursor placed at the location on the map and then write down the coordinates, or use a screen capture tool to take a screenshot, making sure to include the coordinate readout.
If the coordinates don't change as you move around the map, then the Coordinates tool is currently in the point mode. To enable continuous mode, just click the Coordinates icon to the left of the coordinate readout.
To Use the Coordinates of a Point You Click
If you want to copy and paste the coordinates of a specific map location into another program or document, the easiest way is to enable the point mode of operation.
1) Click on the Coordinates icon to the left of the coordinate readout. This switches to point mode.
2) Click the point of interest on the map. The coordinates of the clicked point will be shown in the coordinate readout.
3) Use your mouse to select the text in the coordinate readout, then use your operating system's copy function (Ctrl-C on Microsoft Windows) to copy the coordinates to the clipboard.
4) Use your operating system's paste function (Ctrl-V on Microsoft Windows) to paste the coordinates into another program or document.
To Get Coordinates for a Location in Other Coordinate System Formats
You can obtain map coordinates in either of two coordinate systems:
⚫ Latitude and Longitude (WGS84 datum)
⚫ Alaska Albers Equal Area Conic (NAD83 datum)
The default is latitude and longitude, in decimal degrees. This format will likely be useful in most situations. If you need the latitude and longitude in other formats, you can use this handy converter: http://rumkin.com/tools/gps/degrees.php
The Alaska Albers Equal Area Conic format is a more specialized coordinate format, with the units being Easting and Northing in meters. This is the coordinate system that the land status layers are stored in, and is more applicable for GIS use. This format is likely of not much use to non-GIS users.
1) To select a different coordinate format, move the mouse cursor over the small upward-pointing triangle shown just to the right of the coordinate readout. A menu will pop-up, showing the two coordinate systems that are available. See below for an example.

Move the mouse cursor over the triangle to display a menu
of the available coordinate system formats. Bold text indicates
the currently active coordinate system.
2) Click on the name of the coordinate system that you want to use.
|
|
In the examples above, a point on the Earth is noted as an XY coordinate. X and Y refer to locations within a Cartesian coordinate system, where X identifies a position along the horizontal (X) axis and Y identifies a position along the vertical (Y) axis. •In a geographic coordinate system, longitude is expressed by the X value, and latitude is expressed by the Y value. •In a projected coordinate system, Easting is expressed by the X value, and Northing is expressed by the Y value. ...and Know Your Signs With geographic coordinate systems, it is critically important to understand how north, south, east, and west are represented by the coordinate values. Algebraic signs, plus (+) and minus (-) are used to indicate the compass directions, as such: •North latitude is represented as a positive value (+) •South latitude is represented as a negative value (-) •East longitude is represented as a positive value (+) •West longitude is represented as a negative value (-) |
|
|
Converting between latitude and longitude formats Latitudes and longitudes can be expressed in several different formats, such as: •45° 24' 13.4" (Degrees, minutes, seconds) •45° 24.223 (Degrees and decimal minutes) •45.40372222° (Decimal degrees) All three examples above are equivalent, that is, they identify the same spot on the Earth. You may run into situations where you must provide latitude and longitude values in a particular format. For example, you might have a lat/long coordinate in degrees, minutes, and seconds format, but the program you're working with might require you to input the lat/long in decimal degrees format. To do this, you have to convert from one format to another. You can do this using an online lat/long converter. There are many such converters available online, but here's one that's very easy to use: http://rumkin.com/tools/gps/degrees.php This site converts from any of the three formats to any of the other three. |
|
|
Latitude + Longitude + Datum = A Complete Coordinate, aka LLD = Problem Free! Casual use of latitude and longitude positions generally doesn't involve referencing the datum to which the lat/long is tied. However, when dealing with GIS a higher level of precision is required, thus lat/long values must always include the associated datum. When noting lat/long coordinates or giving lat/long coordinates to someone, you must always report the datum which is used by the coordinates. Without the datum information, the user will have to guess which datum your lat/long coordinates are in, and this often leads to misalignment of features. Following are several examples of the correct way to note lat/long coordinates: •45.50, -150.25, NAD27 •45.50 N, 150.25 W, NAD83 •45° 30' 00" N, 150° 15' 00" W, WGS84 Note that for each example, the datum has been specified. A lat/long coordinate should never leave your desk without a datum specified. Remember: LLD = Problem Free! |
The Region 7 Land Mapper was developed, and is maintained by, the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service, Region 7, Division of Realty. Questions, comments,and suggestions should be directed to ak_realty@fws.gov
This page was last updated: Thursday, March 13, 2025